MANAGERIAL ROLES
Managers are the people who plan, organize, lead, and control the activities of the organization so that its goals can be achieved. Managerial roles talks about the roles managers play in the organization. Henry Mintzberg identified three major roles of a manager as follows:
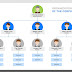
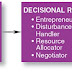
In interpersonal roles, the manager is responsible for managing relationships within and outside the organization. The manager must play a role as a figurehead, a leader and a liaison. In informational roles, the manager is responsible for gathering and distributing information to the stakeholders of the organization. Types of informational roles are monitor, disseminator, and spokesperson. Finally, in decisional roles, the manager is reponsible for processing information and reaching conclusions. Types of decisional roles are entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator and negotiator. (Refer to your notes for explanation on the different types of roles.)
MANAGERIAL SKILLS (MANAGEMENT SKILLS)
Being a manager is not an easy task as he/she is not only required to perform a job well, he/she is also required to manage, direct and motivate his/her subordinate to perform their job well. Therefore, being a manager requires a certain set of skills.
There are three levels of managers namely first-line managers, middle level managers and top level managers. First line managers supervise the individuals who are directly responsible for producing the organization’s product or delivering its service. They carry the title production supervisor, section chief. Middle level managers supervises first-line managers or staff department. They carry titles such as marketing manager or department head. Top level managers provide the strategic direction for the organization. They carry titles such as CEO, CFO, CIO or executive vice president.
The figure below indicates the skills managers must have and the degree of importance for each level of managers.
Conceptual skills is the ability to analyze complex information. It enables managers to process information about the internal/external environment of the organization and determine its implications. Top level managers need to have strong conceptual skills if they are to effectively accomplish goals.
Human skills is the ability to work effectively with people. It involves motivating and disciplining employees, monitoring performance, providing feedback, improving communication and instructing employees. Human skills are most important for middle managers as these managers must coordinate efforts of the members in his group as well as other work groups within the organization.
Technical skills is the knowledge and the ability to use tools, techniques and procedures that are specific to their particular field. Technical skills tend to be most important for first line managers as they must have the knowledge and the "know-how" to ensure that the products and services of their organization are delivered to customer.
Hopefully I have cleared up the confusion between these two terms. Remember, managerial roles are the roles that managers play in the organization while managerial skills are the set of skills required by managers to be effective managers.